It will take about 3 minutes to finish reading this article.
1. nil in Objective-C
1.1 The Concept
nil (or Nil) in Objective-C is a pointer to an empty object. In Objective-C, an object can be an instance or a class. When an object is created, it is allocated to memory and initialized to zero. If it is not initialized to another value, the object pointer has a value of nil.
In Objective-C, sending a message to a nil object is valid because the message does not result in any operation. This is because Objective-C messaging is implemented through method calls that send messages to objects, not through the methods of the objects themselves. So when the object is nil, calling the object’s methods has no effect because it is essentially a null pointer.
Here’s an example showing the use of nil in Objective-C:
1 | NSString *str = nil; |
Output results:
1 | The value of str is: (null) |
1.2 Implementation Principle
In terms of the underlying implementation, nil in Objective-C is actually a predefined macro for a null object pointer. In Objective-C, all objects are accessed via pointers, and a nil is actually a pointer with a value of zero. Thus, when an object is assigned a value of nil, it is actually given a pointer with a value of 0, indicating that the object does not exist.
1 | #define nil __DARWIN_NULL |
‘__DARWIN_NULL’ is a null pointer constant pointing to a null address, defined in <stddef.h> with the following code:
1 | #define __DARWIN_NULL ((void *)0) |
Thus, in Objective-C, when we use nil, we are actually using a null pointer constant to a null address for a null object pointer.
2. nil in Swift
2.1 The Concept
In Swift, nil is not a pointer to an empty object. It represents a special type that lacks a value, which is not limited to objects. In Swift, you can use nil to represent any type of value, including basic data types (such as Int, Double, etc.) as well as object types.
nil in Swift is used for optional types. If a variable or constant is declared as an optional type, it can either contain a value or be nil. if an attempt is made to forcibly unwrap (i.e., get the actual value of) a variable or constant of an optional type, and the variable or constant currently has the value of nil, the program will crash.
Here’s an example showing the use of nil in Swift:
1 | var str: String? = nil |
Output results:
1 | The value of str is: nil |
The above code will report an error if it is changed to the following:
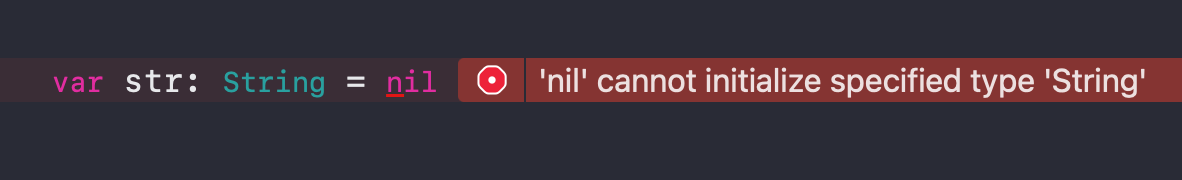
1 | var str: String = nil |
Or
1 | var str = nil |
The error messages are as follows:
Or
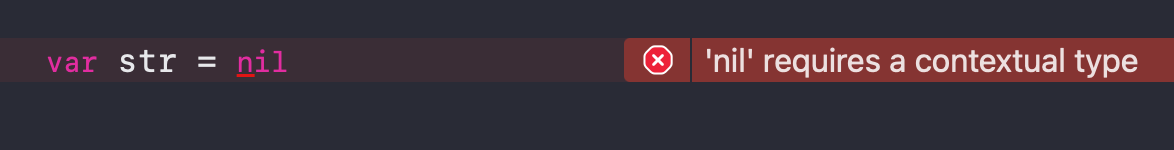
That’s because in Swift, the types of variables and constants must be explicitly specified at declaration time. When we declare a variable or constant and initialize it to nil, the Swift compiler can’t determine the type of the variable or constant because nil can represent a missing value of many types. Therefore, we need to tell the compiler the type of the variable or constant by way of a type annotation or type inference.
‘var str: String = nil ‘ declares a variable str of type String and initializes it to nil, but the Swift compiler is not able to determine the type of the variable because nil can represent the missing value of multiple types. As a result, the compiler reports an error, suggesting that we need to provide a Contextual Type or an optional type for it.
2.2 Implementation Principle
In Swift, all types can use optional types to represent the case of missing values. An optional type is actually an enumerated type that has two possible values: a value and no value. When an optional type has a value of nil, it is actually a special enum member that indicates that the value is missing.
1 | enum Optional<T> { |
Output results
1 | The value of str is nil |
3. Conclusion
In Objective-C, nil represents a pointer to a null object, which is used to indicate that the object does not exist. In Swift, nil represents a missing value and can be used to represent any type of value. In terms of the underlying implementation, nil in Objective-C is a predefined macro that represents a pointer to a null object, while nil in Swift is a special type that represents the case of an optional type (enumerated type) that is missing a value. In practice, developers need to choose the appropriate language and data type to indicate the presence or absence of a value according to different situations to ensure the correctness and stability of the program.